Since its outbreak in China in December and detection of the first case in Bangladesh in early March, Covid-19 has caused massive economic losses through unprecedented communication disruptions worldwide. The pandemic is going to have multiple negative effects on business operations, particularly industries, manufacturing facilities, financial services and supply chains, although they are yet to be fully understood.
Like other countries, Bangladesh has taken several policy measures that are mostly focussed on granting or arranging soft loans to help businesses meet working capital requirements and payment of employee salaries. The banking sector, responsible for executing the stimulus packages, does not have enough strength to cope up with new burdens. However, the incentive packages may help the businesses to tackle initial shocks of the crisis.
The Covid-19 broke out at a time when the Bangladesh economy was growing at a faster pace and the country was in a transition of graduating to a middle income country. In that context, it is important to draw a national strategy to revive the economy alongside saving lives from the onslaught of the coronavirus through proper health management.
The country's capital market can be utilised in fighting the economic downturn caused by the pandemic. Globally central banks, capital market regulators and stock exchanges are taking initiatives to support governments in tackling the situation by redressing approach, products, features and services. Despite limitations of our capital market, some untapped windows can be utilised with national strategy to address the bleak economic outlook.
Capital market platform, especially the bond market, can support all types of corporates, financial institutions and business ventures through quick accumulation of funds from different active and inactive sources. Existing equity platform may also come up with suitable fast track products or procedure through some modifications in the regulatory structure.
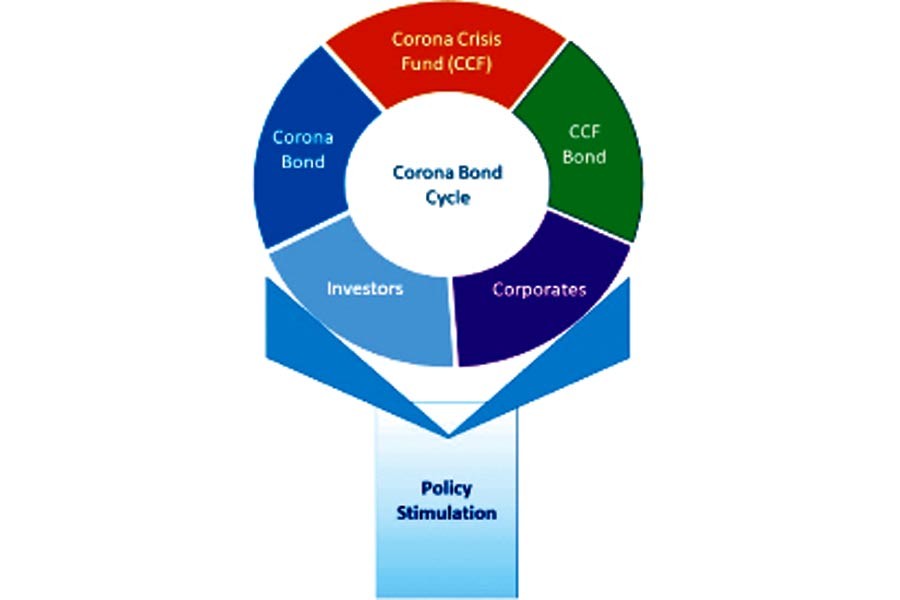
Bond market platform can be used in offering some new products and features for mobilising resources to support reconstruction and revitalisation of the corona-affected economy. Although our corporate bond market is almost absent, a new rule is under process of implementation. The draft rule, if finalised with proper regulations, may ensure a vibrant bond market. A trajectory in this regard is mentioned below:
CORONA BOND SERIES: Some countries are working on corona bond. In Bangladesh, such a new and specialised, stimulus bond series (may be titled Corona Bond-1, Corona Bond-2, Corona Bond-n etc.) can be issued in next three years with a target of raising Tk 1.0 trillion. The government or any government agency or the government and any international agency together may be the issuer of such bond. Size of the first issue may be Tk 200 billion. Subsequent issues may be launched depending on success of the first one.
Proceeds of the bond may be kept in a fund styled Corona Crisis Fund (CCF), which can be utilised in purchasing a set of corporate bonds (may be named as CCFx Bond, CCFy Bond, CCFn Bond etc.) issued by corporates, banks, non-bank financial institutions, microcredit institutions, and other eligible associations and institutions under a set of criteria. To make the whole process effective and functioning, an aggressive set of stimulus packages may be attached with corona bonds and CCF bonds. Investments of CCF bonds may also be done offering incentives. The bonds of the basket may be recycled into other financing module including equities.
Corporates may be allowed to offer equities, if appropriate, through initial public offering (IPO) or private placement to redeem the bond issued to CCF or CCF-authorised organisations.
The basic idea is to create a velocity of investments in the private sector through involvement of the government. It will offset immediate cash burden on the government of subsidising or bailing out businesses and corporates.
The regulator and stock exchanges may offer rapid processing of corona bonds with similar concept and terms. However, without the government's intervention regarding redemption and settlement of such bonds, it will not give expected results.
FC BOND: The government or any government agency or the government and any international agency together may issue a Foreign Currency (FC) bond to generate foreign currency to speed up development works and also finance possible deficit in foreign exchange earnings due to global impacts of Covid-19.
Non-resident Bangladeshis (NRBs), international agencies, multinational corporations (MNCs), local corporates with export quota, and local individuals with undisclosed foreign sources of money may be target investors of the bond. Investment can be made in the government's mega projects like Padma Bridge, Metro Rail, and Karnaphulli Tunnel. The bond may have multi-FC feature to ensure flexibility along with multi-stimulus future benefits and convertible feature offering equity stakes in government projects.
SOCIAL BOND: One or more social bonds may be offered to public and private limited companies, high-net-worth individuals (HNIs), social agencies and international agencies. The proceeds of the bond may be utilised by the governments in different social sectors such as emergency medical research, vaccines, education, agriculture, and small businesses that would be affected by the coronavirus crisis. It may help the government maintain or repair or build social infrastructures for revitalising the economy. Such bonds have already been issued by some multilateral agencies in the wake of the pandemic.
The social bond may zero interest bearing and bond holders may be offered future incentives such as tax rebate, tax exemption, special tax reduction, and priority future investment opportunities; It may be repaid in five to seven years. All types of investors - business and non-business, individuals and corporates, national and multilateral agencies - may be the target investors. Religious and charitable domestic and international agencies may also be encouraged through marketing ultimate objectives of the venture.
To implement multi-stimulus recycling model technique for mobilising financing through a series of government and private sector bonds, a broad-based policy framework from the Bangladesh Bank is required. Coordination between capital market regulators, stock exchange and commercial banks is also inevitable to materialise the initiative. Dhaka Stock Exchange (DSE) can be engaged in managing the whole process, as the key coordinator. Implementation of the bond mechanism such as corona crisis bond and social bond is not possible without policy supports from the government.
UTILISING EQUITY MARKET: Equity platform of the capital market can also be used with the same objective to support corporate entities which would be affected by the coronavirus crisis.
A fast track Initial Public Offering (IPO) process can be initiated to support genuine entrepreneurs who need equity funding, who are truly affected by Covid-19 and who have potential to bounce back.
As a parallel process, a fast track IPO approval method may be introduced under certain conditions like : (a) No placement shareholders in the pre-IPO capital structure; (b) all pre-IPO shareholders will be considered as sponsors and restrictions will be imposed on offloading sponsor shares; (c) sponsors will be allowed to sell shares, after lock-in period is over, to other sponsors only; (d) issuer will submit an independent valuation of shares under three acceptable methods at the time of application, based on which price of IPO will be recommended and approved by the exchange and the commission respectively; (e) buy back policy may be introduced to protect the general investors.
Submission of application of the fast track IPO with all requisite documents has to be electronically processed to the commission and the exchange simultaneously. On the following day, a presentation on the submitted application and documents will be held in front of representatives of the commission and exchanges by the issuer and issue manager. The commission and the exchange, within five working days immediately after the date of presentation shall initiate enquiries from respective ends. The exchange will have to intimate the commission upon each enquiry. Within this period the commission and/or the exchange may have a physical visit at the premises, production centres, revenue centres and offices.
The issuer will also have to reply to enquiries from the exchange and the commission within next three working days; and the exchange will submit recommendations within five working days to the commission. The commission will issue approval based on the recommendation of the exchange within three days and communicate the decision to the applicant. Within this period the commission may require the issuer and issue manager to give a final presentation before the commission and the exchange.
The prime objective of the fast track IPO would be rapid financing to the issuer without making the IPO investors' interest at risk.
Covid-19 is drastically changing the economic and financial landscape. Without changing approach and mechanism within the structure, it would be difficult to overcome the crisis. Only the government initiative will not sufficient to face economic and social impacts of the pandemic and a national initiative involving public and private sectors is essential. The capital market platform may be used as an effective tool in the process.
Shaifur Rahman Mazumdar is Chief Operating Officer at Dhaka Stock Exchange Ltd.
The views expressed in this article are author's own and do not represent the DSE position.